Case study –
This is a case study. Case studies are not timed separately. You can use as much exam time as you would like to complete each case. However, there may be additional case studies and sections on this exam. You must manage your time to ensure that you are able to complete all questions included on this exam in the time provided.
To answer the questions included in a case study, you will need to reference information that is provided in the case study. Case studies might contain exhibits and other resources that provide more information about the scenario that is described in the case study. Each question is independent of the other questions in this case study.
At the end of this case study, a review screen will appear. This screen allows you to review your answers and to make changes before you move to the next section of the exam. After you begin a new section, you cannot return to this section.
To start the case study –
To display the first question in this case study, click the Next button. Use the buttons in the left pane to explore the content of the case study before you answer the questions. Clicking these buttons displays information such as business requirements, existing environment, and problem statements. When you are ready to answer a question, click the Question button to return to the question.
Background –
You are a developer for Proseware, Inc. You are developing an application that applies a set of governance policies for Proseware’s internal services, external services, and applications. The application will also provide a shared library for common functionality.
Requirements –
Policy service –
You develop and deploy a stateful ASP.NET Core 2.1 web application named Policy service to an Azure App Service Web App. The application reacts to events from Azure Event Grid and performs policy actions based on those events.
The application must include the Event Grid Event ID field in all Application Insights telemetry.
Policy service must use Application Insights to automatically scale with the number of policy actions that it is performing.
Policies –
Log policy –
All Azure App Service Web Apps must write logs to Azure Blob storage. All log files should be saved to a container named logdrop. Logs must remain in the container for 15 days.
Authentication events –
Authentication events are used to monitor users signing in and signing out. All authentication events must be processed by Policy service. Sign outs must be processed as quickly as possible.
PolicyLib –
You have a shared library named PolicyLib that contains functionality common to all ASP.NET Core web services and applications. The PolicyLib library must:
- Exclude non-user actions from Application Insights telemetry.
- Provide methods that allow a web service to scale itself.
- Ensure that scaling actions do not disrupt application usage.
Other –
Anomaly detection service –
You have an anomaly detection service that analyzes log information for anomalies. It is implemented as an Azure Machine Learning model. The model is deployed as a web service. If an anomaly is detected, an Azure Function that emails administrators is called by using an HTTP WebHook.
Health monitoring –
All web applications and services have health monitoring at the /health service endpoint.
Issues –
Policy loss –
When you deploy Policy service, policies may not be applied if they were in the process of being applied during the deployment.
Performance issue –
When under heavy load, the anomaly detection service undergoes slowdowns and rejects connections.
Notification latency –
Users report that anomaly detection emails can sometimes arrive several minutes after an anomaly is detected.
App code –
EventGridController.cs –
Relevant portions of the app files are shown below. Line numbers are included for reference only and include a two-character prefix that denotes the specific file to which they belong.

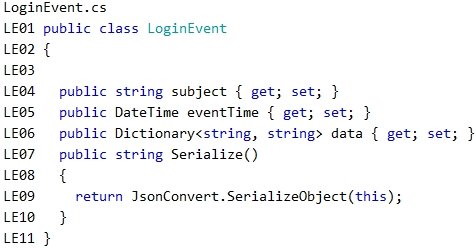
LoginEvent.cs –
Relevant portions of the app files are shown below. Line numbers are included for reference only and include a two-character prefix that denotes the specific file to which they belong.
Question 1.
DRAG DROP –
You need to implement the Log policy.
How should you complete the Azure Event Grid subscription? To answer, drag the appropriate JSON segments to the correct locations. Each JSON segment may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes to view content.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Select and Place:
Correct Answer:

Box 1:WebHook –
Scenario: If an anomaly is detected, an Azure Function that emails administrators is called by using an HTTP WebHook. endpointType: The type of endpoint for the subscription (webhook/HTTP, Event Hub, or queue).
Box 2: SubjectBeginsWith –
Box 3: Microsoft.Storage.BlobCreated
Scenario: Log Policy –
All Azure App Service Web Apps must write logs to Azure Blob storage. All log files should be saved to a container named logdrop. Logs must remain in the container for 15 days.
Example subscription schema –
{
“properties”: {
“destination”: {
“endpointType”: “webhook”,
“properties”: {
“endpointUrl”: “https://example.azurewebsites.net/api/HttpTriggerCSharp1?code=VXbGWce53l48Mt8wuotr0GPmyJ/nDT4hgdFj9DpBiRt38qqnnm5OFg==”
}
},
“filter”: {
“includedEventTypes”: [ “Microsoft.Storage.BlobCreated”, “Microsoft.Storage.BlobDeleted” ],
“subjectBeginsWith”: “blobServices/default/containers/mycontainer/log”,
[1]
“isSubjectCaseSensitive “: “true”
}
}
}
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/event-grid/subscription-creation-schema
Question 2.
You need to ensure that the solution can meet the scaling requirements for Policy Service.
Which Azure Application Insights data model should you use?
A. an Application Insights dependency
B. an Application Insights event
C. an Application Insights trace
D. an Application Insights metric
Application Insights provides three additional data types for custom telemetry:
Trace – used either directly, or through an adapter to implement diagnostics logging using an instrumentation framework that is familiar to you, such as Log4Net or
System.Diagnostics.
Event – typically used to capture user interaction with your service, to analyze usage patterns.
Metric – used to report periodic scalar measurements.
Scenario:
Policy service must use Application Insights to automatically scale with the number of policy actions that it is performing.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-monitor/app/data-model
Question 3.
DRAG DROP –
You need to implement telemetry for non-user actions.
How should you complete the Filter class? To answer, drag the appropriate code segments to the correct locations. Each code segment may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Select and Place:
Correct Answer:

Scenario: Exclude non-user actions from Application Insights telemetry.
Box 1: ITelemetryProcessor –
To create a filter, implement ITelemetryProcessor. This technique gives you more direct control over what is included or excluded from the telemetry stream.
Box 2: ITelemetryProcessor –
Box 3: ITelemetryProcessor –
Box 4: RequestTelemetry –
Box 5: /health –
To filter out an item, just terminate the chain.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-monitor/app/api-filtering-sampling
Question 4
DRAG DROP –
You need to ensure that PolicyLib requirements are met.
How should you complete the code segment? To answer, drag the appropriate code segments to the correct locations. Each code segment may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Select and Place:
Correct Answer:

Scenario: You have a shared library named PolicyLib that contains functionality common to all ASP.NET Core web services and applications. The PolicyLib library must:
✑ Exclude non-user actions from Application Insights telemetry.
✑ Provide methods that allow a web service to scale itself.
✑ Ensure that scaling actions do not disrupt application usage.
Box 1: ITelemetryInitializer –
Use telemetry initializers to define global properties that are sent with all telemetry; and to override selected behavior of the standard telemetry modules.
Box 2: Initialize –
Box 3: Telemetry.Context –
Box 4: ((EventTelemetry)telemetry).Properties[“EventID”]
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-monitor/app/api-filtering-sampling
